As summer rolls around, lawmakers in Washington are preparing to vote on a jobs bill that would include $1 billion for summer jobs for teens. Much of the urgency for the program stems from the private-sector plunge in summer jobs for teenagers over the past few years. It’s no secret that the recession walloped teens’ jobs as much as it did their parents. But some economists find the clamor for public jobs programs a little ironic, given last year’s midrecession minimum wage increase, which may have reduced teen employment even beyond the recessionary drop.
Before the minimum wage jumped to $ 7.25 an hour last summer, University of California-Irvine economist David Neumark estimated that it would lead to an additional 300 000 job losses for teens and young adults. The 2009 wage increase was set in motion in a better labor market in May 2007, when Congress voted to boost the minimum from $ 5.15 an hour to $ 7.25 an hour over the course of the next two years.
It’s hard to parse the jobs lost because of the recession and those lost because of the minimum wage increase--there’s no direct evaluation of the impact of the wage increase yet--but it’s likely that raising the wage floor contributed to the record-high teen unemployment rates, Neumark says. "Almost everyone accepts that minimum wages decrease employment or likely increase unemployment of the least-skilled," he says. Neumark advocated for delaying last year’s increase.
The unemployment rate for teenagers was 25.4 percent in April, compared with 9.9 percent overall, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Teens generally have higher unemployment rates. In November 2007, the month before the start of the recession, the unemployment rate for the overall population was 4. 7 percent, versus 16. 2 percent for workers aged 16 to 19. Teen employment has been declining for some time. The percentage of teens with jobs has fallen from about 57 percent in 1989 to about 40 percent in 2007 (both dates reflect healthy economies). The reasons are diverse. For one thing, increased school enrollment appears to account for about a third of that decline, according to the Economic Policy Institute. "For teens, there has been a remarkable long-term shift from summer employment to summer enrollment," reports EPI economist Heidi Shierholz.
One of the critical issues for job-seeking teens is the changing face of the competition, which is increasingly skilled. "Not only are they competing with each other for available positions, but they are competing with recent college graduates and job seekers who have two or more years of on-the-job experience and are willing to take almost any position that provides a steady paycheck," says John Challenger of outplacement firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas.
Why is it hard to analyze the jobs lost()
A. Because there’s no data showing the impact of the wage increase
B. Because the minimum wages decrease employment rates
C. Because there are some unstable factors
D. Because summer employment has shifted to summer enrollment

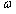 ,则沿地球表面运行的人造地球卫星的周期为____________;某地球同步通讯卫星离地面的高度H为____________。
,则沿地球表面运行的人造地球卫星的周期为____________;某地球同步通讯卫星离地面的高度H为____________。